Indoor Positioning for Mobile Robots
Thanks to UWB technology, robots can now navigate indoors with centimeter-level precision. The project was carried out at PIAP Lukasiewicz, a leading Polish government defence research institute.
A novel approach to solving the challenge of Indoor positioning for mobile robots with UWB technology. The system automatically transitions between GNSS and UWB based on signal quality and availability, ensuring continuous positioning accuracy.
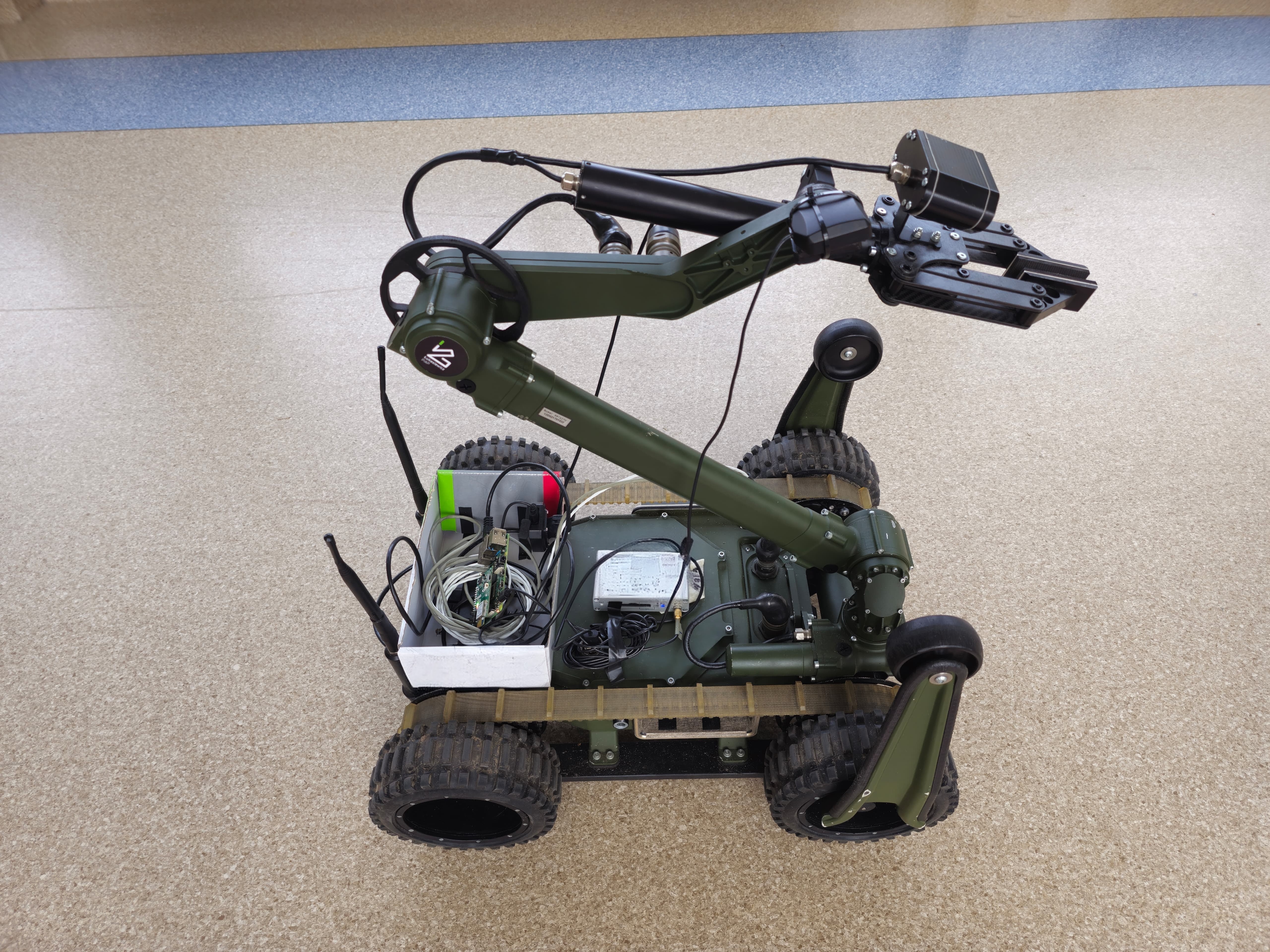

System Overview
The project addresses the limitations of traditional GNSS in indoor environments by integrating UWB technology for centimeter-level precision. The system automatically transitions between GNSS and UWB based on signal quality and availability, ensuring continuous positioning accuracy.
Key features include:
- Seamless transition between indoor and outdoor navigation
- Centimeter-level positioning accuracy indoors
- Integration with existing GNSS systems
- Real-time position tracking and visualization
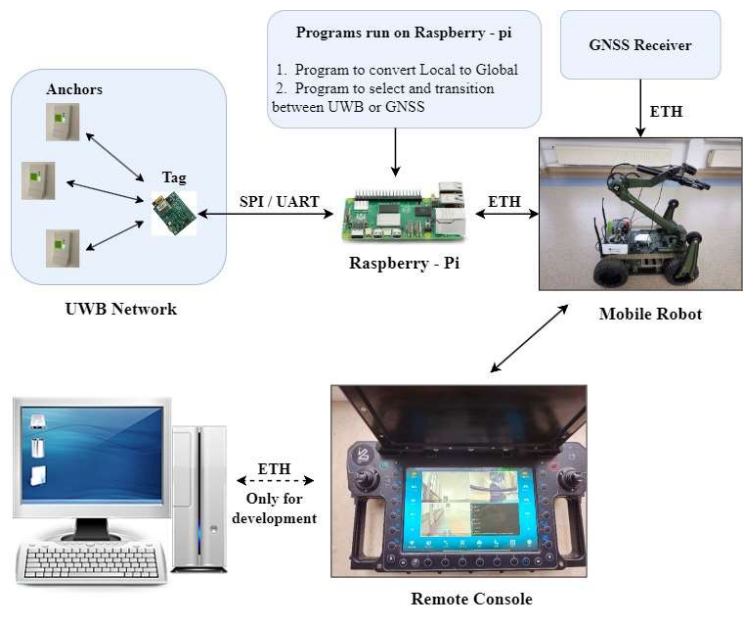
Technical Implementation
The system utilizes Qorvo’s UWB modules configured as anchors and tags. The anchors are strategically placed in the indoor environment, while tags are mounted on mobile robots. A Raspberry Pi processes the positioning data and converts local coordinates to global coordinates using the Haversine formula.
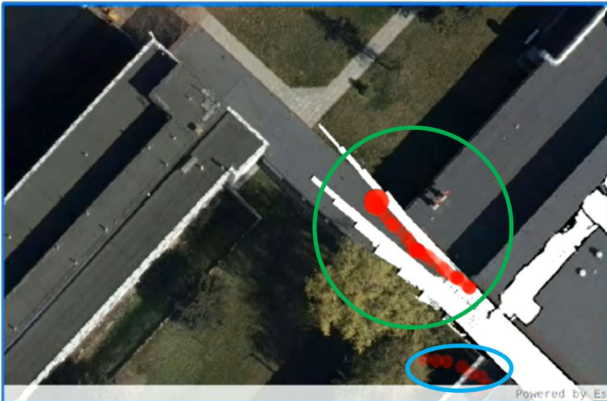
Results and Performance
Testing demonstrated superior positioning accuracy in indoor environments using UWB compared to GNSS:
- Stable positioning in indoor corridors (shown in green)
- Successful automatic transition to GNSS outdoors
- Reliable performance in GNSS-challenged environments
- Real-time position updates with minimal latency

Network Configuration Guidelines
For optimal UWB network performance:
- Symmetric module arrangement
- 10m spacing between rows
- Variable height placement for Z-axis coverage
- Strategic anchor positioning for maximum coverage
The project successfully demonstrates the feasibility of seamless indoor-outdoor navigation for mobile robots, opening new possibilities for autonomous navigation in complex environments.